Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hattori, Takanori; Suzuki, Koji*; Miyo, Tatsuya*; Ito, Takayoshi*; Machida, Shinichi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1059, p.168956_1 - 168956_9, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)Radial collimators (RC) with a 0.5 mm gauge size (GS) were specially designed for high-pressure neutron diffraction experiments and their performance and efficacy were investigated. The RCs with nominal GS of 0.75 mm, 1.5 mm, and 3.0 mm effectively exhibited GS of 0.50 mm, 1.07 mm, and 2.78 mm, respectively. The transmissions of all three RCs were almost equivalent. The assessment using a P-E press and a DAC revealed that the anvil scattering was considerably minimized and the sample-to-anvil signal ratio reached values of 0.5 and 2.0 for the PE press and DAC, respectively, when using the 0.5 mm-GS RCs. These results indicate that the 0.5mm-GS RCs have been fabricated as intended and exhibit efficacy for the high-pressure-neutron diffraction experiments, specifically those exceeding 30 GPa. Among those ever manufactured for neutron scattering experiments, the RCs display the smallest GS.
 to 34 GPa
to 34 GPaKlotz, S.*; Casula, M.*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori
Physical Review B, 100(2), p.020101_1 - 020101_5, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:52.56(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Ytterbium dihydride (YbH ) shows a well-known transition at
) shows a well-known transition at  16 GPa from a CaH
16 GPa from a CaH -type structure to a high-pressure (high-
-type structure to a high-pressure (high- ) phase with Yb at hcp sites and unknown H-positions. Here, we report its complete structure determination by neutron diffraction at 34 GPa. Hydrogen(deuterium) is located at 2
) phase with Yb at hcp sites and unknown H-positions. Here, we report its complete structure determination by neutron diffraction at 34 GPa. Hydrogen(deuterium) is located at 2 and 2
and 2 positions of space group
positions of space group 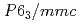 , thus forming a high-symmetry "collapsed" close-packed lattice. The transition is sluggish and can be seen as a transfer of 1/2 of the hydrogen atoms from strongly corrugated H-layers to interstitial sites of the Yb-lattice. We demonstrate by first-principles calculations that the transition is related to a change from a completely filled
, thus forming a high-symmetry "collapsed" close-packed lattice. The transition is sluggish and can be seen as a transfer of 1/2 of the hydrogen atoms from strongly corrugated H-layers to interstitial sites of the Yb-lattice. We demonstrate by first-principles calculations that the transition is related to a change from a completely filled  -electron configuration to a fractional
-electron configuration to a fractional  -hole (
-hole ( 0.25 h) occupation in the high-
0.25 h) occupation in the high- phase. The
phase. The 
 charge transfer closes the gap at the transition and leads to a metallic ground state with sizeable electron-phonon interaction involving out-of-plane vibrational modes of interstitial hydrogen.
charge transfer closes the gap at the transition and leads to a metallic ground state with sizeable electron-phonon interaction involving out-of-plane vibrational modes of interstitial hydrogen.
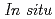 neutron diffraction of iron hydride in iron-silicate-water system under high pressure and high temperature condition
neutron diffraction of iron hydride in iron-silicate-water system under high pressure and high temperature conditionIizuka, Riko*; Yagi, Takehiko*; Goto, Hirotada*; Okuchi, Takuo*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami
Hamon, 27(3), p.104 - 108, 2017/08
Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the solar system and is considered to be one of the promising candidates of the light elements in the Earth's core. However, the amount of hydrogen dissolved in the core and its process are still unknown because hydrogen cannot be detected by X ray and easily escapes from iron at ambient conditions. In this study, we have conducted high-pressure and high-temperature in-situ neutron diffraction experiments on the iron-hydrous mineral system using PLANET in J-PARC. We observed that the water, which was dissociated from a hydrous mineral, reacted with iron to form both iron oxide and iron hydride at about 4 GPa. Iron hydride remained stable after further increase in temperature. This formation occurred at 1000K, where no materials melted. This suggests that hydrogen dissolved into iron before any other light elements dissolved in the very early stage of the Earth's evolution.

Sakai, Hironori; Kato, Harukazu; Tokunaga, Yo; Kambe, Shinsaku; Walstedt, R. E.; Nakamura, Akio; Tateiwa, Naoyuki*; Kobayashi, Tatsuo*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 15(28), p.S2035 - S2037, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:21.31(Physics, Condensed Matter)The cubic-fluorite type uranium dioxide UO is an ionically bounded insulator with localized magnetic moments of U
is an ionically bounded insulator with localized magnetic moments of U (5
(5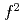 ) ions. Under atmospheric pressure, UO
) ions. Under atmospheric pressure, UO exhibits a first order antiferromagnetic transition at
exhibits a first order antiferromagnetic transition at  =30.8 K accompanied by a small lattice distortion. In order to clarify the interrelation between QQ and exchange interactions in this system, we performed d.c. magnetization measurement under high pressure up to about 1 GPa by a piston-cylinder-type cramped cell. From the d.c. magnetization measurements under high pressure (
=30.8 K accompanied by a small lattice distortion. In order to clarify the interrelation between QQ and exchange interactions in this system, we performed d.c. magnetization measurement under high pressure up to about 1 GPa by a piston-cylinder-type cramped cell. From the d.c. magnetization measurements under high pressure (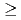 0.1 GPa), it is found that UO
0.1 GPa), it is found that UO shows a weak-ferromagnetic-like transition at
shows a weak-ferromagnetic-like transition at  30 K, where the transition temperature is almost independent of external pressure up to 1 GPa. The ferromagnetic component per uranium atom is very small (
30 K, where the transition temperature is almost independent of external pressure up to 1 GPa. The ferromagnetic component per uranium atom is very small (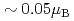 ), although its component is dependent of pressure. This small ferromagnetic component may come from a canted antiferromagnetic ordering.
), although its component is dependent of pressure. This small ferromagnetic component may come from a canted antiferromagnetic ordering.
Okubo, Tsutomu; Araya, Fumimasa
Proceedings of International Workshop on Current Status and Future Directions in Boiling Heat Transfer and Two-Phase Flow, p.177 - 181, 2000/00
no abstracts in English
Kawamura, Seiko; Hattori, Takanori; Kambara, Wataru*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kawamura, Seiko; Hattori, Takanori; Kambara, Wataru*
no journal, ,
Hattori, Takanori; Suzuki, Koji*; Miyo, Tatsuya*; Ito, Takayoshi*; Machida, Shinichi*
no journal, ,
Radial collimators (RC) with a 0.5 mm gauge size (GS) were specially designed for high-pressure neutron diffraction experiments and their performance and efficacy were investigated. The RCs with nominal GS of 0.75 mm, 1.5 mm, and 3.0 mm effectively exhibited GS of 0.50 mm, 1.07 mm, and 2.78 mm, respectively. The transmissions of all three RCs were almost equivalent. The assessment using a P-E press and a DAC revealed that the anvil scattering was considerably minimized and the sample-to-anvil signal ratio reached values of 0.5 and 2.0 for the PE press and DAC, respectively, when using the 0.5 mm-GS RCs. These results indicate that the 0.5mm-GS RCs have been fabricated as intended and exhibit efficacy for the high-pressure-neutron diffraction experiments, specifically those exceeding 30 GPa. Among those ever manufactured for neutron scattering experiments, the RCs display the smallest GS.